Welcome to our weekly feature, where every Saturday we break down popular Web3 concepts and simplify them for you. If this newsletter was forwarded to you, feel free to subscribe by clicking the button below.
Cryptocurrencies have become increasingly popular in recent years, with Bitcoin and Ethereum being among the most well-known examples. These digital assets are decentralized, meaning that they are not controlled by any central authority or government. Instead, they are secured using cryptographic techniques such as cryptographic signatures and hash functions.
What are Cryptographic Signatures?
Cryptographic signatures are mathematical techniques used to verify the authenticity of digital data. In the context of cryptocurrencies, a signature is used to confirm the ownership of a particular cryptocurrency address, allowing for secure transactions without the need for a trusted third party.
When a user initiates a cryptocurrency transaction, their digital signature is used to verify that they are the owner of the funds being sent. This signature is created by using a private key, which is a secret code known only to the owner of the cryptocurrency address. The private key is used to create a digital signature that is unique to the transaction, providing a secure way to transfer funds without the need for a trusted third party.
Once the transaction has been signed, it is broadcast to the network of nodes that make up the cryptocurrency's blockchain. Each node then verifies the transaction using the sender's public key, which is available to everyone on the network. This ensures that only the owner of the private key associated with the sending address can initiate transactions, preventing fraudulent activities such as double-spending.
The use of cryptographic signatures ensures that transactions are secure and that funds cannot be stolen or misappropriated. This is particularly important in the context of cryptocurrencies, which are not backed by any physical assets and are therefore vulnerable to hacking and fraud.
Hash functions are also an important part of the security infrastructure of cryptocurrencies. Hash functions are mathematical algorithms that take input data and produce a fixed-size output called a hash. This hash is unique to the input data and can be used to verify the integrity of the data. In the context of cryptocurrencies, hashes are used to create unique identifiers for each transaction, making it impossible for anyone to alter the transaction history without being detected.
Each transaction is hashed, creating a unique identifier that is added to the blockchain. This creates a permanent, tamper-proof record of the transaction history, preventing any alterations or fraud. Because the hash of each transaction is dependent on the data in the transaction, any alteration to the transaction data would result in a different hash. This would be immediately detected by the network of nodes, ensuring the integrity of the transaction history.
The use of hash functions in cryptocurrencies provides a high level of security, making it difficult for anyone to tamper with the transaction history. However, it is important to note that hash functions are not foolproof and can be vulnerable to attacks such as collision attacks. In a collision attack, an attacker can create two different pieces of data that produce the same hash. While collision attacks are rare, they are a potential vulnerability that should be considered when designing cryptographic systems.
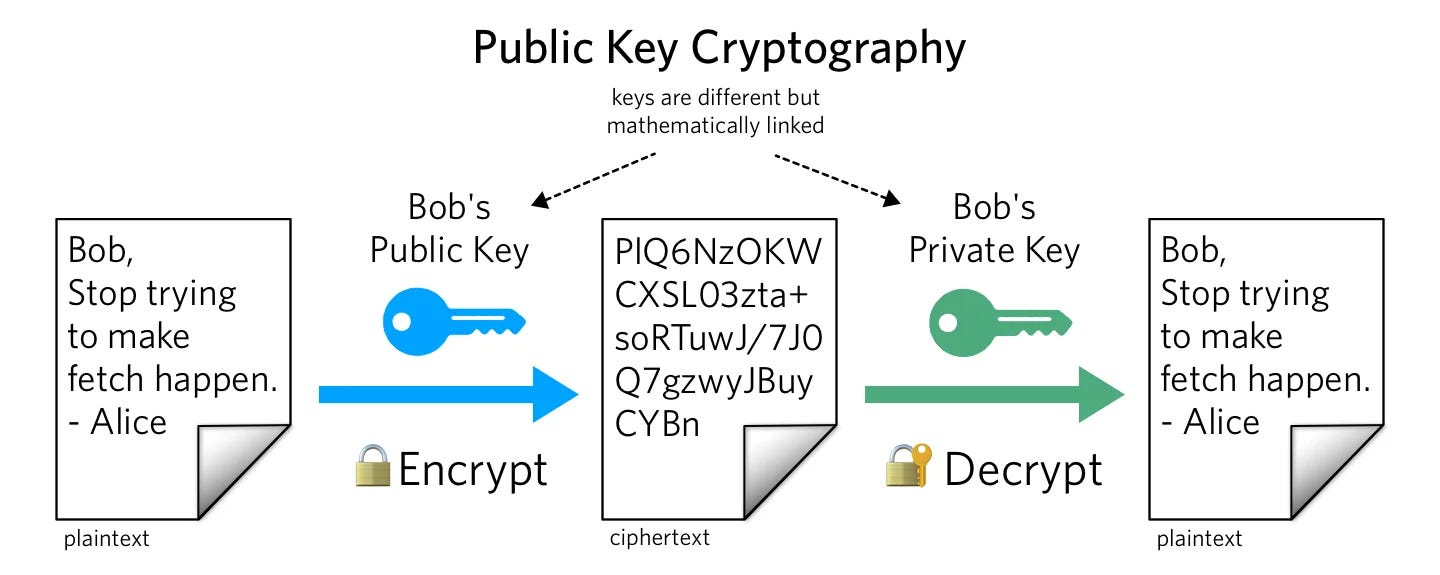
In addition to the use of cryptographic signatures and hash functions, cryptocurrencies are also secured through the use of public key cryptography. Public key cryptography is a technique that uses a pair of keys, one public and one private, to encrypt and decrypt data. The public key is available to everyone on the network, while the private key is kept secret by the owner of the address.
When a user sends cryptocurrency to another address, they use the recipient's public key to encrypt the transaction data. The recipient can then use their private key to decrypt the data and access the funds. This ensures that only the owner of the private key associated with the receiving address can access the funds, providing a secure way to transfer funds without the need for a trusted third party.
The use of public key cryptography in cryptocurrencies provides a high level of security, making it difficult for anyone to access funds without the appropriate private key. However, it is important to note that the security of public key cryptography relies on the strength of the underlying encryption algorithms. If these algorithms were to be compromised, the security of public key cryptography would be weakened.
In summary, cryptographic signatures, hash functions, and public key cryptography are all important components of the security infrastructure of cryptocurrencies. These techniques work together to ensure that transactions are secure and that funds cannot be stolen or misappropriated. The use of these techniques provides a high level of security, making it difficult for attackers to compromise the integrity of the transaction history or gain access to funds without the appropriate private key.
As cryptocurrencies continue to gain in popularity, it is likely that new techniques will be developed to enhance their security even further. However, it is important to note that no system is completely foolproof, and there is always the potential for vulnerabilities to be discovered. It is therefore essential for developers and users of cryptocurrencies to stay informed about the latest security techniques and to take appropriate measures to ensure the security of their digital assets.
In conclusion, cryptographic signatures and hash functions are essential components of the security infrastructure of cryptocurrencies. These techniques provide a high level of security, ensuring that transactions are secure and that funds cannot be stolen or misappropriated. While no system is completely foolproof, the use of these techniques provides a strong foundation for the security of cryptocurrencies, allowing them to be used as a secure and reliable means of transferring value.
If you’d like to support us, send tokens to fomofix.eth
DISCLAIMER:
None of this is financial advice. This newsletter is strictly educational and is not investment advice or a solicitation to buy or sell any assets or to make any financial decisions. Please be careful and do your own research.